By: nlp-yurovskiy-kirill.co.uk
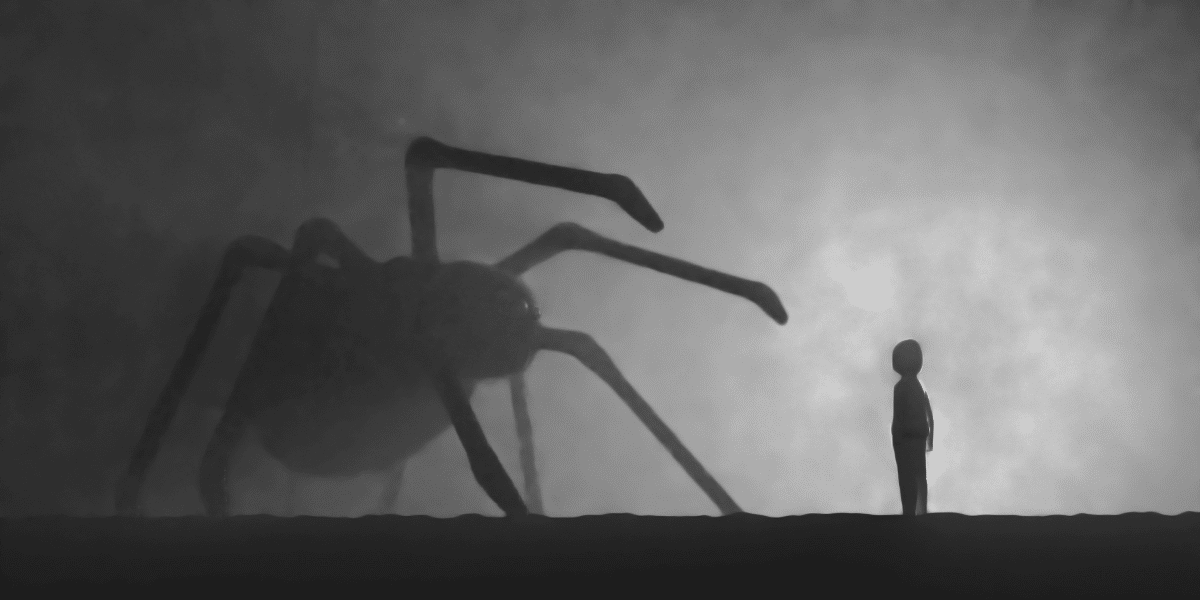
We all experience fear and anxiety at certain points in our lives. These emotions can act as vital warning signals, alerting us to potential threats or dangers. However, when fears become excessive or irrational, they can spiral into overpowering phobias that severely restrict our lives. About 19 million Americans suffer from phobias or irrational, persistent fears of certain objects or situations.
People with phobias often go to great lengths to avoid the source of their fear, which can disrupt their daily routines, limit their experiences, and prevent personal growth. The fears may seem irrational, but the anxious thoughts and physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, sweating, and nausea are very real.
Conventional treatments like exposure therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy can be effective, but they require substantial time and mental effort. What if you could “reprogram” your mind to overcome fears using neuro linguistic programming (NLP) techniques? This mind-body approach may provide powerful tools for conquering phobias.
Understanding the Neuro Linguistic Connection
NLP is a field that explores the relationship between our neural processes (neuro), language and communication patterns (linguistics), and behavior and emotions (programming). It looks at how our minds process the world through our five senses and how we use language, both internal and external, to represent and shape our experience of reality.
“Language is not just a mode of communication, it is a force that shapes our experience of the world around us and even our subjective internal experience,” explains Kirill Yurovskiy, an NLP trainer. “By understanding how language influences thought patterns, we can reshape our perceptions and behaviors.”
The core principle of NLP is that our minds operate through deeply ingrained patterns and programs, many of which were formed in early childhood. These mental programs determine how we filter and process information from our environment through our senses. They also shape our values, beliefs, and behaviors – including our fears and phobias.
For example, if you had a traumatic experience involving a dog as a child, your brain may have formed neural associations linking dogs with danger. You might unconsciously filter information to detect potential “threats” from dogs, fueling anxious thoughts and physiological responses consistent with your fear. More info: https://nlp-yurovskiy-kirill.co.uk/
NLP offers techniques to interrupt these patterns and install new, more empowering programs to eliminate fears. Here are some of the most powerful strategies:
Anchoring and Resource State
One widely used NLP technique is anchoring, which aims to recreate or “anchor” desirable emotional states and then apply them to diffuse fearful situations. The anchoring process involves:
- Recalling a memory or focusing on an anchor stimulus (like a particular touch or sound) that gives you an intense feeling of confidence, calm, or well-being.
- In that resourceful state, you practice applying it to imagined scenarios related to your fear through visualization.
- Eventually, you learn to fire off the resourceful state on demand to counteract the anxious state when confronted with the actual fear stimulus.
“It’s all about disrupting the neural pathways around the phobic response by interjecting a new stimulus consistently paired with a more positive emotional state,” explains Dr. Michael Briers, anxiety researcher and NLP practitioner. “The goal is to forge new neural connections so the stimuli no longer triggers the old programmed fear response.”
Visual/Kinesthetic Dissociation
This imaginative NLP technique helps people gain psychological distance and perspective on their phobias, making them feel less threatening. It involves visualizing your feared object or situation, then imagining yourself moving further away from it. Or you may visualize shrinking the object down to a tiny size to make it feel harmless and insignificant.
“The idea is to disrupt how you unconsciously represent the threat in your mind’s eye and felt sense, diffusing the intensity of the fear and anxiety response,” says Yurovskiy. “Performing this dissociation mentally first makes the actual exposure to feared stimuli easier to handle.”
Reimprinting Experiences
Certain NLP strategies aim to go back and “rewrite” or reimprint the original experiences that coded the phobic response. One such technique is called the Visual/Kinesthetic Dissociation (VKD) protocol, which involves the following steps:
- Recall the original traumatic memory that formed the fear.
- Dissociate from it by visualizing yourself watching the event unfold from a safe, detached perspective.
- Give the visualized younger “you” the understanding, skills and resources to better handle the situation without encoding a lasting fearful response.
- Finally, have the younger “you” re-experience the memory utilizing those new empowering resources and perspectives.
“The goal is to update that old programmed response from your childhood by fully re-processing the traumatic experience through your current, more capable mindset,” says Briers. “It’s a way to essentially ‘hack’ back into your neural programming.”
Mapping Across Senses
Since our experiences are coded through multiple sensory inputs, shifting how we represent an experience in one sense modality can affect our experiences in others. The NLP technique of mapping across senses plays on this connection:
If you have a phobia linked to a particular visual stimulus, like snakes, you may be asked to imagine the visual representation becoming distorted, faded or darkened. As you alter the visual representation, you’ll notice spontaneous changes in how you represent the fear in your other senses like sound or feeling.
“All the sensory representations of your phobic experience are mapped and linked in your neural coding,” notes Yurovskiy. “By disrupting just one key sensory representation, you can radically alter and potentially diffuse the whole multi-sensory fear experience.”
The Language Factor
Much of NLP deals with deconstructing and reframing how we internally represent experiences through language. This applies to our self-talk or internal narratives as well as our interpretations and labels around external events.
For instance, someone with a phobia of public speaking may have an internal voice saying “I’m going to mess up and embarrass myself horribly when I have to talk.” A practitioner would help rephrase this as a less catastrophic hypothetical like “I may feel a little nervous, but I’ve prepared well and can get through this.”
“Our internal language codes our experiences and defines our realities,” says Briers. “By reorganizing and updating the language, you update the programmed neuro-associations and responses.”
Putting It Into Practice
While the basic NLP techniques sound straightforward, fully updating and retraining our neural programs takes practice and guidance. Many find it most effective to work through phobias and deep-seated fears with a trained NLP practitioner or counselor.
As with any therapeutic approach, NLP has its critics who challenge its scientific validity and claim of producing long-lasting transformation by rewiring the brain. Like many self-directed psychological change methods, its effectiveness relies heavily on an individual’s willingness, commitment and perseverance in utilizing the techniques.
However, many who have used NLP strategies report overcoming profound fears and phobias that had severely restricted their lives for years. Some say it allowed them to finally confront and conquer phobias that had proven impervious to other therapeutic approaches.
While NLP remains somewhat controversial, the neuroscience community is increasingly recognizing the profound links between our language patterns, mental representations, and our subjective experiences and behaviors. Research is steadily revealing how our conscious minds can influence neural plasticity and rewire engrained mental programs and habit patterns.
By understanding these connections, NLP provides a powerful framework for people to potentially reprogram their neural processes, release phobic responses, and create new perceptual filters to experience life with more freedom and psychological resilience.
So if you’re feeling held back by overpowering fears or phobias, it may be worth exploring whether updating your mental “programming” through NLP techniques can help you conquer your mind’s irrational constraints.
Published By: Aize Perez