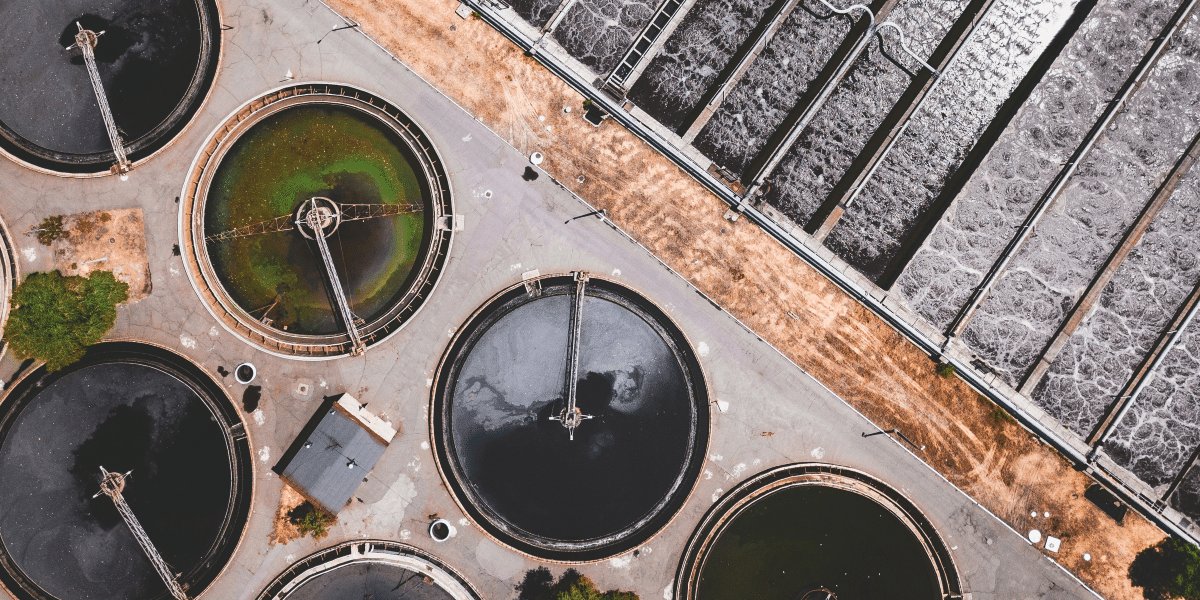
New Hampshire, known for its picturesque landscapes and pristine natural environments, is also home to a diverse range of septic systems. As state regulations evolve and environmental concerns intensify, the management and installation of septic tanks in New Hampshire have undergone significant changes. This article explores the evolution of septic tank regulations in New Hampshire, the impact on homeowners and the industry, and emerging trends that are shaping the future of septic systems in the state.
Historical Context of Septic Regulations in New Hampshire
Historically, septic tank regulations in New Hampshire have been influenced by both environmental protection goals and the practical needs of homeowners. Early regulations were relatively lax, focusing primarily on ensuring basic functionality and preventing obvious public health hazards. However, as environmental awareness grew and the impact of septic systems on water quality became more evident, regulatory frameworks began to tighten.
In the 1990s, New Hampshire implemented more stringent standards for septic system design and installation, driven by concerns over groundwater contamination and the health of surface waters. These changes aimed to address issues related to aging infrastructure, increasing population density, and the need to protect the state’s abundant natural resources.
Current Regulatory Landscape
As of the latest updates, septic tank regulations in New Hampshire are governed by the Department of Environmental Services (NHDES), which enforces rules designed to safeguard water quality and public health. Key aspects of the current regulatory landscape include:
- Advanced Treatment Requirements: New Hampshire now requires advanced treatment systems for properties located in areas with high-density development or those situated near sensitive water bodies. These systems, such as aerobic treatment units (ATUs) or nitrogen-reducing systems, are designed to provide more effective wastewater treatment and reduce the risk of nutrient pollution.
- Regular Inspections and Maintenance: Regulations mandate regular inspections of septic systems, typically every three years, to ensure proper operation and maintenance. Homeowners are responsible for arranging these inspections and addressing any issues identified. Failure to comply can result in fines and costly repairs.
- Separation Distances and Setbacks: New Hampshire enforces strict separation distances between septic systems and water sources, such as wells and surface waters. These setbacks are intended to prevent contamination and protect drinking water quality. The specific distances vary depending on factors like soil type and system design.
- Pump-Out Requirements: Homeowners are required to pump out their septic tanks periodically, generally every 1 to 3 years, depending on usage and system type. This maintenance helps prevent overflows and system failures, which can lead to costly repairs and environmental damage.
Impact on Homeowners
For homeowners in New Hampshire, the evolving septic tank regulations have both direct and indirect impacts. While the intention behind these regulations is to protect water quality and public health, they also bring about several challenges:
- Increased Costs: The adoption of advanced treatment systems and the requirement for regular inspections can increase the overall cost of septic system maintenance and replacement. Homeowners may face higher upfront costs for advanced systems and ongoing expenses for inspections and pump-outs.
- Property Values: Compliance with stringent septic regulations can affect property values. Homes with newer, advanced septic systems may command higher prices, while properties with outdated or non-compliant systems might face reduced market value or difficulty in selling.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the regulatory requirements can be complex, particularly for new homeowners or those unfamiliar with septic system maintenance. It often requires time, effort, and financial resources to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Industry Response and Innovations
The septic system industry in New Hampshire has adapted to changing regulations and market demands through various innovations and improvements. These include:
- Technology Integration: The industry has seen a rise in the use of advanced technologies to improve system performance and compliance. Smart septic systems, equipped with sensors and remote monitoring capabilities, allow for real-time tracking of system performance and early detection of potential issues. This technology helps homeowners manage their systems more effectively and avoid costly failures.
- Eco-Friendly Solutions: In response to environmental concerns, the industry is increasingly focusing on eco-friendly solutions. Innovations such as nitrogen-reducing systems and constructed wetlands are designed to minimize environmental impact while providing effective wastewater treatment. These solutions cater to the growing demand for sustainable and environmentally responsible septic systems.
- Educational Efforts: To help homeowners understand and comply with regulations, the industry has invested in educational initiatives. Workshops, informational resources, and online tools are available to provide guidance on septic system maintenance, regulatory requirements, and practices.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
Looking ahead, several emerging trends are likely to shape the future of septic systems in New Hampshire:
- Enhanced Regulatory Frameworks: As environmental protection remains a priority, regulations are expected to continue evolving. Future updates may focus on further reducing nutrient pollution, addressing emerging contaminants, and enhancing system efficiency. Homeowners and industry professionals will need to stay informed about these changes and adapt accordingly.
- Integration with Green Infrastructure: There is a growing interest in integrating septic systems with green infrastructure solutions, such as rain gardens and permeable pavements. These approaches aim to manage stormwater and wastewater more effectively, reducing the burden on traditional septic systems and improving overall environmental sustainability.
- Innovations in Wastewater Reuse: Advances in wastewater reuse technologies are gaining traction, with the potential to reduce the volume of wastewater that needs treatment. Reusing greywater for non-potable purposes, such as irrigation, can help alleviate the strain on septic systems and promote water conservation.
- Climate Change Adaptation: The impacts of climate change, such as increased rainfall and flooding, are influencing septic system design and management. Future innovations may focus on adapting systems to withstand extreme weather events and mitigate potential damage.
Conclusion
The landscape of septic tank regulations and practices in New Hampshire has evolved significantly over the years, reflecting a growing commitment to environmental protection and public health. While these changes present challenges for homeowners and the industry, they also drive innovation and improvement in septic system technology and management. By staying informed about regulatory updates, embracing advanced technologies, and adopting eco-friendly solutions, homeowners can navigate the complexities of septic system maintenance and contribute to the preservation of New Hampshire’s natural resources. As regulations continue to evolve and new trends emerge, the septic system industry in New Hampshire will play a crucial role in balancing the needs of residents with the imperative to protect the environment.
Published By: Aize Perez